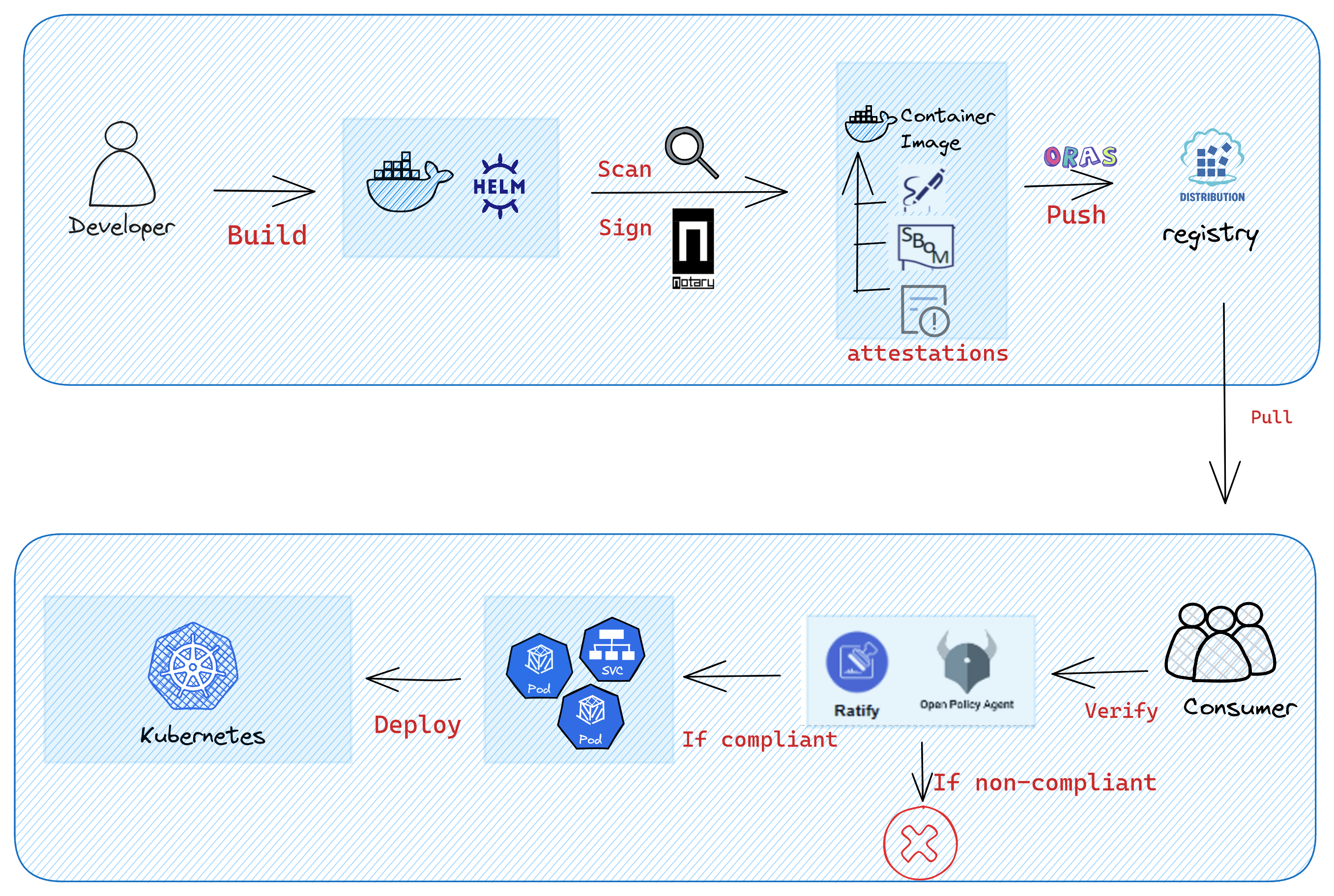
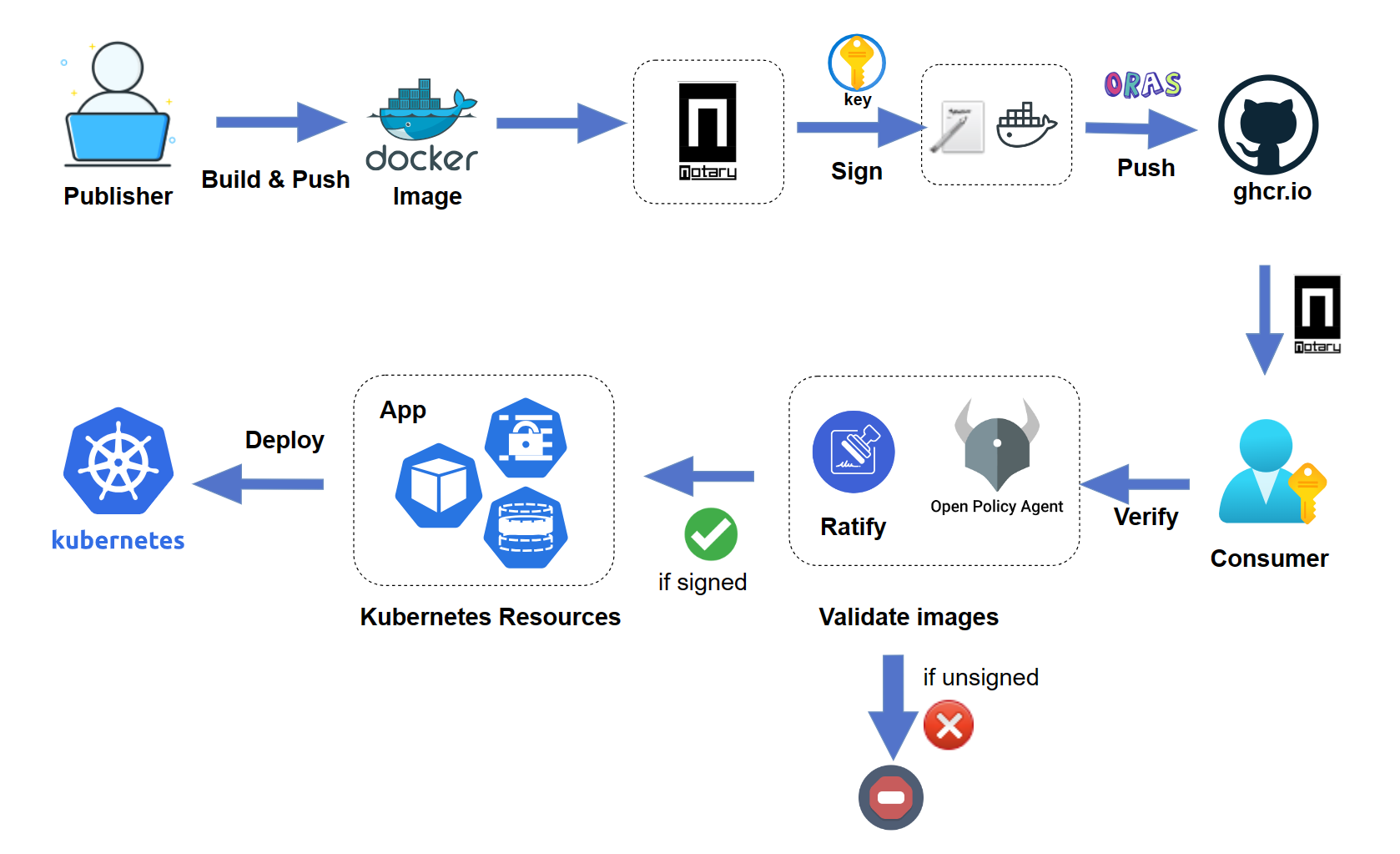
The signed container images enable users to assure deployments are built from a trusted entity and verify images haven't been tampered with since their creation. The signed image ensures integrity and authenticity before the user pulls an image into any environment and avoid attacks.
Notation is a standards-based tool and library for signing and verifying OCI artifacts. It generates signatures and associates them with OCI artifacts to ensure integrity for the supply chain.
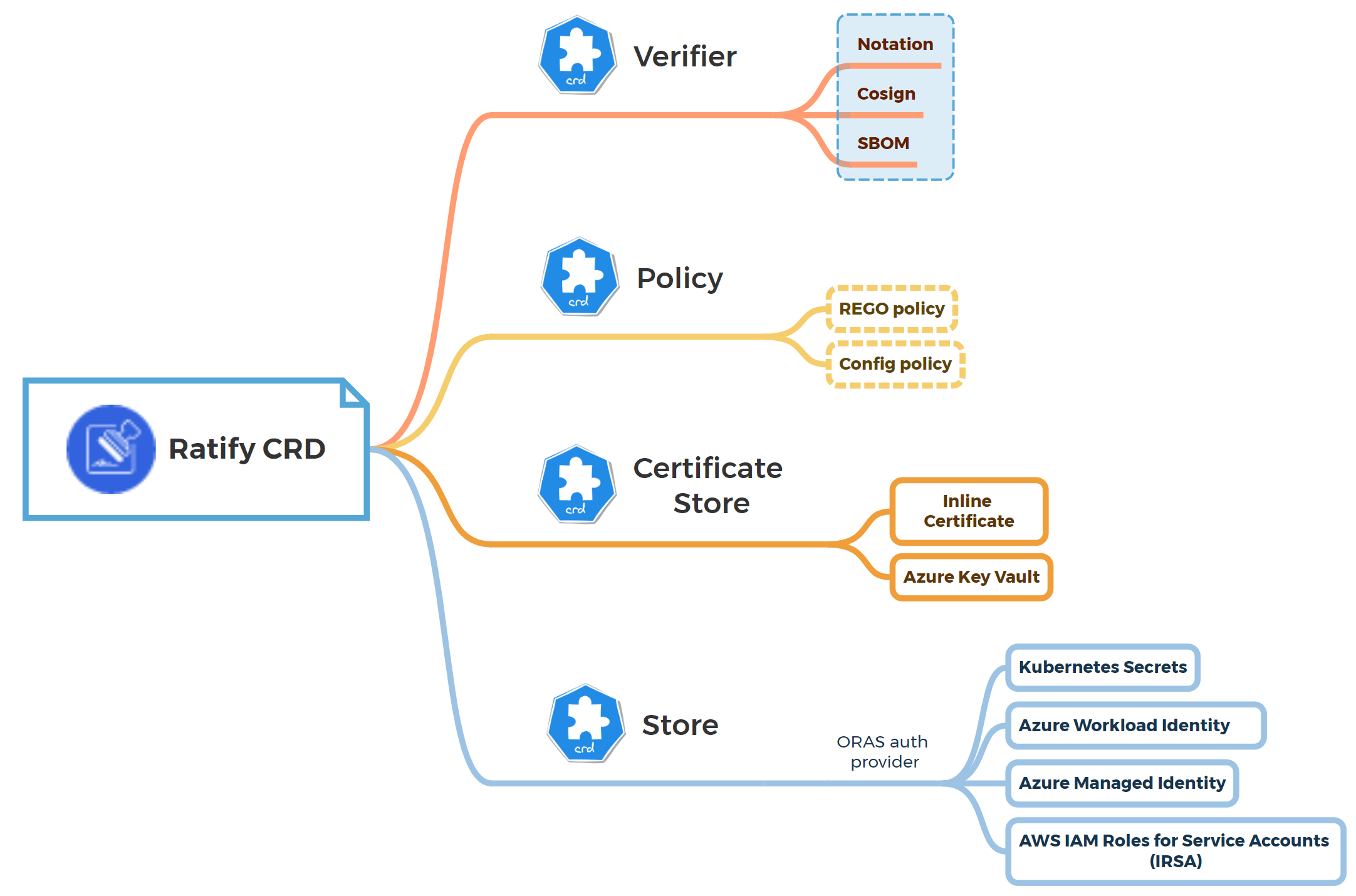
Ratify is a verification engine as a binary executable and on Kubernetes which enables verification of artifact security metadata and admits for deployment only those that comply with policies you create. It works with OPA Gatekeeper to provide fine-grained admission policy control capabilities for application deployment on Kubernetes.
This article walks you through the following end-to-end workflow:
- Build and sign an image in GHCR as a software publisher
- Verify the signed image as a software consumer
- Validating and enforcing only signed images are allowed to be deployed on Kubernetes
The typical scenario is when you want to secure your containerized package for a GitHub repository, you can apply this workflow to your project to ensure image integrity between software publisher and consumer.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes v1.20 or higher (You can use minikube if you are new to Kubernetes)
- Helm v3
Create an OCI-compatible registry
Create and run an OCI-compatible registry on your development computer using the distribution/distribution with the image deletion enabled. The following command creates a registry that is accessible at localhost:5001.
docker run -d -p 5001:5000 -e REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED=true --name registry registry
Add an image to the registry
The following commands build and push the wabbit-networks/net-monitor container image to your container registry. Notation supports OCI v1.1 and v1.0 compliant registries. In this article, we use ghcr.io as a sample registry.
docker build -t localhost:5001/net-monitor:v1 https://github.com/wabbit-networks/net-monitor.git#main
Log in to ghcr.io with Docker. You can follow this guide to get the your personal GitHub Token.
echo $CR_PAT | docker login ghcr.io -u $YOUR_USER_NAME --password-stdin
Push the image to ghcr.io. You can record the image digest from the output.
docker push ghcr.io/$namespace/net-monitor:v1
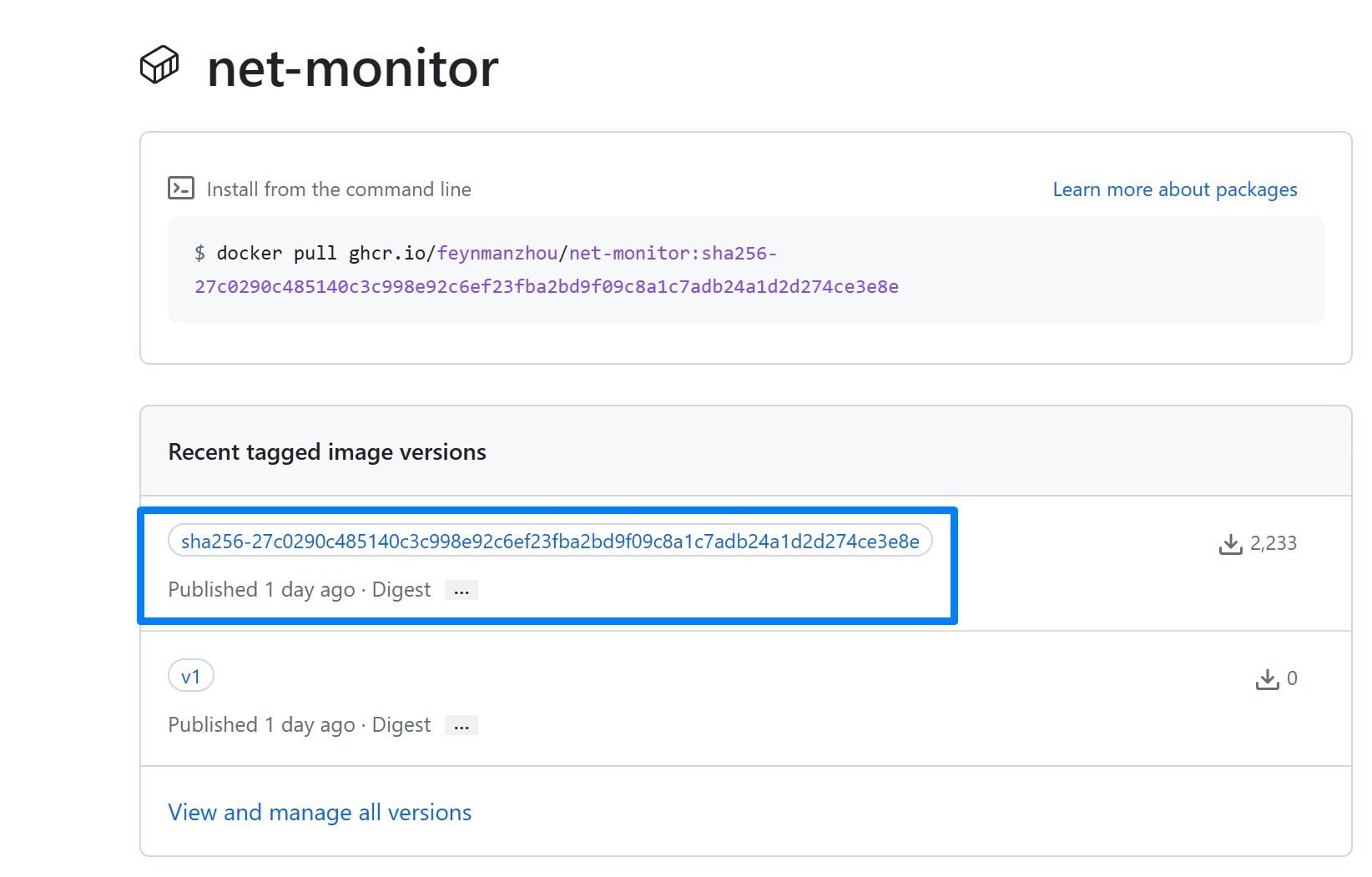
You can record the image digest from the output. For example, the image digest is ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/net-monitor@sha256:27c0290c485140c3c998e92c6ef23fba2bd9f09c8a1c7adb24a1d2d274ce3e8e. Set the environment variable for this image digest.
IMAGE=ghcr.io/$namespace/net-monitor@sha256:27c0290c485140c3c998e92c6ef23fba2bd9f09c8a1c7adb24a1d2d274ce3e8e
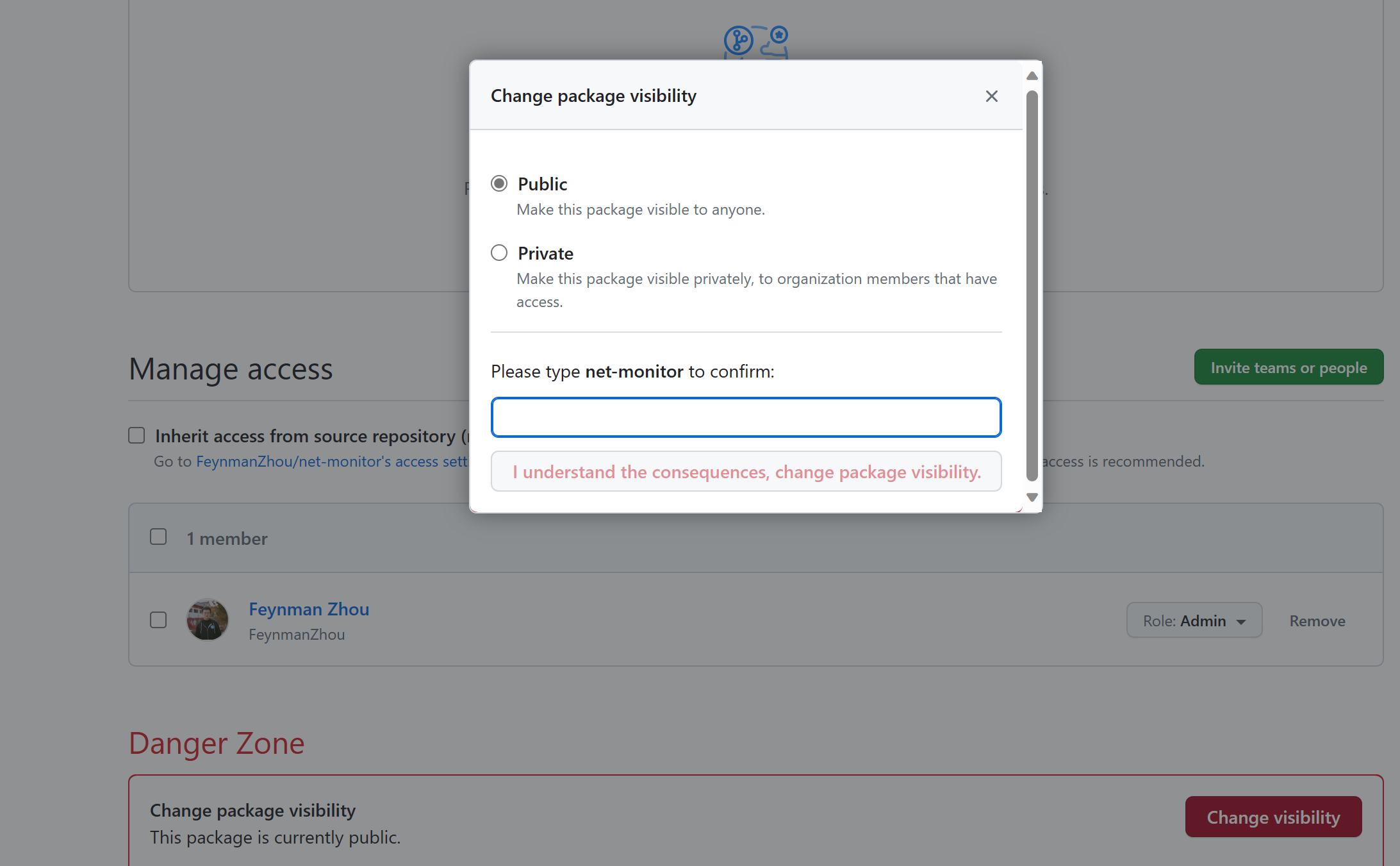
Change the package visibility from private to public on GitHub Package settings. It will allow Notation and Ratify to pull the images from the GHCR registry without authentication configuration. See Configuring a package's access control and visibility for details.
Install Notation CLI
Install the latest version on Linux. Follow the installation guide for other platforms.
curl -LO https://github.com/notaryproject/notation/releases/download/v$NOTATION_VERSION/notation_$NOTATION_VERSION\_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar xvzf -C /usr/bin/ notation
Generate a test key and self-signed certificate
Use notation cert generate-test to generate a test RSA key for signing artifacts, and a self-signed X.509 test certificate for verifying artifacts. Please note the self-signed certificate should be used for testing or development purposes only.
The following command generates a test key and a self-signed X.509 certificate. With the --default flag, the test key is set as a default signing key.
notation cert generate-test --default "ratify-sample.io"
Use notation cert ls to confirm the certificate is stored in the trust store.
Sign the image
Sign the sample image with the flag --signature-format to use COSE signature format. in ghcr.io.
notation sign --signature-format cose $IMAGE
The generated signature is pushed to the registry and the digest of the container image returned.
Use notation ls to show the signature associated with the container image.
$ notation ls $IMAGE
ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/net-monitor@sha256:27c0290c485140c3c998e92c6ef23fba2bd9f09c8a1c7adb24a1d2d274ce3e8e
└── application/vnd.cncf.notary.signature
└── sha256:f4c1e923d1f2a7b76513c889a0db548a093f422d06ac6b83ce7243e0c8fa7805
You can find the signature has also been pushed to the GHCR registry associated with the signed image.
Create a trust policy
To verify the container image, configure the trust policy to specify trusted identities that sign the artifacts, and level of signature verification to use. For more details, see trust policy spec.
Create a JSON file with the following trust policy, for example:
cat <<EOF > ./trustpolicy.json
{
"version": "1.0",
"trustPolicies": [
{
"name": "ratify-sample-images",
"registryScopes": [ "*" ],
"signatureVerification": {
"level" : "strict"
},
"trustStores": [ "ca:ratify-sample.io" ],
"trustedIdentities": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
EOF
Import the trust policy configuration from a JSON file.
notation policy import ./trustpolicy.json
Verify the image signature as a software consumer
As a consumer, verify the signed image before using it.
You can also check the signature digest and inspect the signature and its certificate information to make sure the image is produced from a trusted identity.
Verify the containe image before deploying to Kubernetes
Try out Ratify in Kubernetes through OPA Gatekeeper as the admission controller. It will enforce only signed images can be deployed to Kubernetes.
Set up Gatekeeper with external data.
helm repo add gatekeeper https://open-policy-agent.github.io/gatekeeper/charts
helm install gatekeeper/gatekeeper \
--name-template=gatekeeper \
--namespace gatekeeper-system --create-namespace \
--set enableExternalData=true \
--set validatingWebhookTimeoutSeconds=5 \
--set mutatingWebhookTimeoutSeconds=2
Install the lastest version of Ratify. Specify the certificate generated by Notation for verification purposes.
helm repo add ratify https://ratify-project.github.io/ratify
helm install ratify \
ratify/ratify --atomic \
--namespace gatekeeper-system \
--set-file notaryCert=ghcr-networks.io.crt
Apply the constrait to enforce Gatekeeper policy to allow only signed images can be deployed on Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f https://ratify-project.github.io/ratify/library/default/template.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://ratify-project.github.io/ratify/library/default/samples/constraint.yaml
Deploy the sample image signed by Notation. Ratify will verify if this image has a valid signature.
$ kubectl run ratify-signed --image=$IMAGE
/net-monitor@sha256:27c0290c485140c3c998e92c6ef23fba2bd9f09c8a1c7adb24a1d2d274ce3e8e
pod/demo created
Check the signature associated with the image.
Deploy an unsigned image to Kubernetes cluster. The deployment has been denied since the image has not been signed and doesn't meet the deployment criteria.
$ kubectl run demo --image=ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/notation/alpine@sha256:1304f174557314a7ed9eddb4eab12fed12cb0cd9809e4c28f29af86979a3c870
Error from server (Forbidden): admission webhook "validation.gatekeeper.sh" denied the request: [ratify-constraint] Subject failed verification: ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/notation/alpine@sha256:1304f174557314a7ed9eddb4eab12fed12cb0cd9809e4c28f29af86979a3c870
Inspect the logs to get the detailed error message from the Ratify Pod.
$ kubectl logs ratify-xxxx -n gatekeeper-system
{
"subject": "ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/notation/alpine@sha256:1304f174557314a7ed9eddb4eab12fed12cb0cd9809e4c28f29af86979a3c870",
"isSuccess": false,
"message": "verification failed: no referrers found for this artifact"
}
···
Deploy a signed image with an expired certificate.
kubectl run sample --image=ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/alpine:latest@sha256:1304f174557314a7ed9eddb4eab12fed12cb0cd9809e4c28f29af86979a3c870
Error from server (Forbidden): admission webhook "validation.gatekeeper.sh" denied the request: [ratify-constraint] Subject failed verification: ghcr.io/feynmanzhou/alpine:latest@sha256:1304f174557314a7ed9eddb4eab12fed12cb0cd9809e4c28f29af86979a3c870
Inspect the logs to get the detailed error message from the Ratify Pod. You can find that verification failed caused by an invalid signature.
{
"isSuccess": false,
"verifierReports": [
{
"isSuccess": false,
"name": "notaryv2",
"message": "an error thrown by the verifier: failed to verify signature, err: signature is not produced by a trusted signer",
···